oxygen delivery devices and flow rates emt
A condition known as hypoxia insufficient oxygen to the body can occur if a person goes without adequate oxygen for an extended period. All high flow systems require humidification.
High Flow Nasal Cannula.

. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates emt Get link. Low flow O2 delivery device 05-6 Lmin. Oxygen Delivery Systems LOW FLOW OXYGEN DEVICES HIGH FLOW OXYGEN DEVICES Cannot deliver constant FiO 2 Maintain constant FiO 2 Flow 6 - 8 Lmin Delivering O 2 at very high flow.
Flow-restricted oxygen-powered ventilation device. These devices deliver a variable inspired oxygen concentration to the patient which depends on the PIFR. Higher flows 4 Lmin make it uncomfortable for the patient.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Changes in level of consciousness. The type of humidification device selected will depend on the oxygen delivery system in use and the patients requirements.
Review Airway Management for the EMT. Connect the oxygen tubing to the regulator do not over tighten the tubing to the regulator. Oxygen Delivery Devices 1 Flow Is A Variable Describing In 2021 Icu Nursing Nursing Tips Critical Care Nursing Pin On Rt Ships Free.
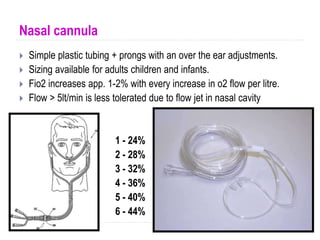
Also called a demand-valve device. The concentration of oxygen delivered to a victim through rescue breathing is 16 percent. Low flow device Most common device used for mild hypoxia Can be set between 1 and 6 LPM 24 to 40 FiO2 FiO2 increases approximately 4 with each liter of O2 KorupoluR GJ Needham DMContemporary CriticalCare.
How much oxygen does the simple face mask deliver. The humidifier should always be placed at a level below the patients head. Is most effective with a flow rate of 15 LPM and can deliver O 2 concentration as high as 90.
Same as Salter with added benefit of providing higher flow rate and. Start studying EMT - O2 delivery tanks rates and masks. A one-way valve between the mask and the reservoir bag prevents the patient from inhaling expired air.
Delivers 100 O2 no need for squeezing to ventilate. Most common delivery device in LTC. Increased breathing and heart rate.
It is NOT the Lmin stated on the venturi that is delivered to the patient. The relationship between the two is as follows. Pulse delivery systems have settings typically.
The percentage of oxygen delivery depends on the flow rate and the delivery device. 6 to 10 lpm. Other sets by this creator.
Many people are familiar with the terminology of 2 or 3 LPM flow. Oxygen therapy can be delivered using a low flow or high flow system. Oxygen flow.
Nasal Cannula 1-6 litersminute 25-50 Humidifier recommended for all flow rates 4 litersminute High Flow Nasal Cannula 1-15 litersminute 25-50 High. The NC can deliver an inspiratory oxygen fraction FIO2 of 24-40 at supply flows ranging from 1-5. Liters per minute or LPM on the other hand refers to the flow rate of continuously flowing oxygen via a continuous or traditional oxygen delivery system.
This oxygen tank duration chart shows approximate usage times for most Oxygen Tank sizes. It can be set to deliver between 10 and 15 Lmin 1 8095 oxygen. These devices deliver a variable inspired oxygen concentration to the patient which depends on the PIFR.
This oxygen tank duration chart shows approximate usage times for most. It consists of a loop of oxygen tubing with 2 prongs that are inserted into a patients nostrils. Designed to entrain a set amount of O2 and air which combine to produce a set flow of O2 the stated on the venturi.
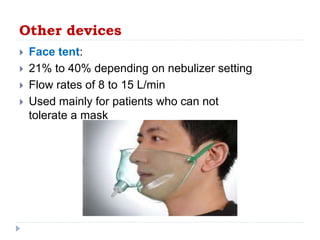
For those who wont tolerate masks. The HFNC is an oxygen-delivery system that includes an airoxygen blender humidifier heater and nasal cannula to deliver precise and very high flow oxygen to your patient. Signs and symptoms of hypoxia include.
Depending on a patients inspiratory effort tidal volume speed of inspiration and respiratory rate the PIFR can often exceed the flow rate at which oxygen or an oxygenair mixture is supplied by the device meaning that at the time of PIFR. The nasal cannula is a low-flow oxygen device provid-ing between 2 6 LPM and a maximum O 2 concentration of about 44. 200969111 Bailey P Thomsen GE Spuhler VJ et alCrit Care MedJan2007351139145.
Flow rate should be 1-6 lpm. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates emt Get link. What is the flow rate of the simple face mask.
Adjust the liter flow. Hospital masks that do provide high flow may start at 15 - 25 Lmin with the ability to entrain 5 - 20 Lmin of room air in a venturi mix to satisfy the patients minute volume requirement. FIO2 depends on the patients pattern of breathing.
The available devices include the non-rebreather mask nasal cannula and the Bag Valve Mask BVM. The device chosen will depend on the patient requirements you found during your Initial Assessment. Low flow device Most common device used for mild hypoxia Can be set between 1 and 6 LPM 24 to 40 FiO2 FiO2.
The fixed performance devices were assessed using the oxygen flow rates for the appropriate inserts as. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates emt Get link. The variable performance devices were tested at oxygen flow rates of 2 4 6 8 10 and 15 lmin 1 as delivered by an AHE ball flow meter.
A high flow device must be able to provide for the patients total minute volume while maintaining a stable oxygen concentration.

Ems Oxygen Admin Flowchart Flow Chart Oxygen Lung Cleanse

Nurse Accessories Supplies Equipment Icu Nursing Emergency Nursing Pharmacology Nursing

Respiratory Sounds Respiratory Sounds Emt Study Nursing Student Tips

Oxygen Delivery Systems Nasal Cannula Flow 1 Emergency Nursing Pediatric Nursing Nursing Student Tips

Oxygen Delivery Devices Ppt Video Online Download

Oxygen Delivery Devices Chapter 10 Diagram Quizlet

Oxygen Delivery Systems Nasal Cannula Flow 1 Emergency Nursing Pediatric Nursing Nursing Student Tips

Oxygen Delivery By Device Nasal Cannula Indicated Practical Nursing Nursing School Prerequisites Nursing School Tips

Oxygen Delivery Devices 1 Flow Is A Variable Describing Icu Nursing Nursing Information Emt Study

Low Flow Devices Vs High Flow Devices Support Oxygenation Respiratory Respiratory Therapy Notes Nurse Study Notes Respiratory Therapy